1. Understanding West Nile Virus
Recent news sees the outbreak of West Nile Virus (WNV) grabbing global attention. Transmitted by mosquitoes to birds and infecting humans and mammals, around 80% of human infections are asymptomatic. Human cases mainly occur from July to September when mosquitoes are active. WNV, a flavivirus like dengue and Zika, is a worldwide concern due to potential serious illness. During this period, be vigilant and take preventive measures.
2. Symptoms of Infection
Approximately 20% of WNV infections in humans can give rise to West Nile fever, which is characterized by a diverse array of symptoms including headache, a general feeling of unease or malaise, fever, muscle pain or myalgia, vomiting, the appearance of a rash, fatigue, and eye pain. These symptoms can vary significantly in terms of their intensity and duration. Some individuals may experience relatively mild symptoms that have the potential to resolve on their own over time.
On the other hand, there are those who may exhibit more severe manifestations. In the most extreme cases, the virus can progress to West Nile neuroinvasive disease, which has a profound impact on the nervous system. This can lead to serious conditions such as meningitis, encephalitis, or even paralysis. Thus, early detection and prompt treatment are essential in order to prevent the occurrence of long-term complications that can have a significant negative impact on an individual's health and quality of life.

3. Risk Factors for People
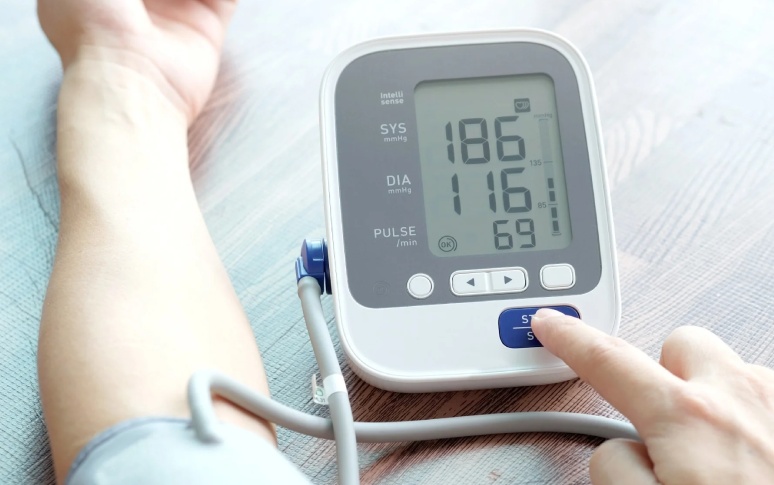
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of severe illness in individuals infected with West Nile virus. These include advanced age, the presence of brain tumors, high blood pressure, blood disorders, diabetes, kidney diseases, alcohol abuse, and genetic factors. People with these conditions are considerably more vulnerable to the virus and are more likely to experience more severe symptoms.
For instance, older adults often have a weaker immune system, making them more susceptible to infections. Similarly, those with underlying health conditions may find it more difficult to recover from the virus. The mortality rate for those who develop West Nile neuroinvasive disease can be as high as 17%, clearly highlighting the seriousness and gravity of this disease.
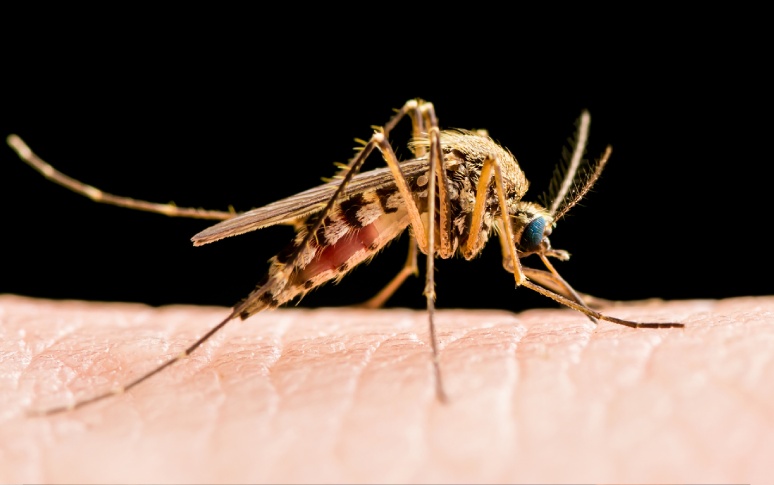
4. How It Spreads
WNV is usually spread to humans through infected mosquitoes, which get the virus from infected birds. As mosquitoes feed on infected birds, they become carriers of the virus. When these mosquitoes then bite humans or other mammals, they can transmit the virus. The virus can also spread between humans through blood transfusion, organ transplant, mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy and breastfeeding, and laboratory exposure. However, these modes of transmission are relatively rare. Preventing mosquito bites is the most effective way to reduce the risk of infection.
5. Vaccination and Treatment
Currently, there is no specific treatment available for West Nile virus infection. The only option available is supportive care, which may involve getting sufficient rest, maintaining proper hydration, and effectively managing symptoms. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary.
As prevention is of utmost importance, this includes taking measures such as avoiding mosquito bites and implementing strategies to reduce mosquito populations. As of now, there is no widely available vaccine for WNV for the general public. Nevertheless, ongoing research is being conducted to develop a vaccine that could potentially provide protection against this virus.

6. Preventive Strategies
Personal protective measures like using mosquito nets, sleeping in screened/air-conditioned rooms, wearing protective clothing and using repellent can reduce the risk of mosquito bites. Eliminating standing water around homes and communities cuts mosquito breeding sites. Public health campaigns raise awareness and encourage preventive steps. Regular surveillance of mosquito populations helps detect the virus early and implement controls.

Was this page helpful? Give us a thumbs up!
